DFCI chief executive Laurie Glimcher, chief operating officer Wi
- NEWS Q&A
Dana-Farber retractions: meet the blogger who spotted problems in dozens of cancer papers
- By
- Max Kozlov

The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston says it is seeking retractions of six papers authored by its researchers.Credit: Craig F. Walker/The Boston Globe via Getty
The prestigious Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) in Boston, Massachusetts, acknowledged this week that it would seek retractions for 6 papers and corrections for an additional 31 — some co-authored by DFCI chief executive Laurie Glimcher, chief operating officer William Hahn and several other prominent cancer researchers. The news came after scientific-image sleuth Sholto David posted his concerns about more than 50 manuscripts to a blog on 2 January.
In the papers, published in a range of journals including Blood, Cell and Nature Immunology, David found images from western blots — a common test for detecting proteins in biological samples — in which bands seemed to be spliced, stretched and copied and pasted. He also found images of mice duplicated across figures where they shouldn’t have been. (Nature’s news team is editorially independent of its publisher, Springer Nature, and of other Nature-branded journals.)

Molecular biologist Sholto David scans the scientific literature for problematic images.Credit: Sholto David.
It was not the first time that some of these irregularities had been noted; some were flagged years ago on PubPeer, a website where researchers comment on and critique scientific papers. The student newspaper The Harvard Crimson reported on David’s findings on 12 January.
The DFCI, an affiliate of Harvard University, had already been investigating some of the papers in question before David’s blogpost was published, says the centre’s research-integrity officer, Barrett Rollins. “Correcting the scientific record is a common practice of institutions with strong research-integrity processes,” he adds. (Rollins is a co-author of three of the papers that David flagged and is not involved in investigations into them, says DFCI spokesperson Ellen Berlin.) The DFCI is declining requests for interviews with its researchers about the retractions.
David, based in Pontypridd, UK, spoke to Nature about how he uncovered the data irregularities at the DFCI and what scientists can do to prevent mix-ups in their own work.
You’ve said that you’re doing data sleuthing full-time. How did you get into it?
I’m not doing anything else. I did my PhD in cellular molecular biology at Newcastle University [UK], and I finished that in 2019. And then I went to work for Oxford Biomedica [a UK gene- and cell-therapy company]. I was there for three years and then I moved out here to Wales. Since then, I’ve been doing this image stuff. I’m not doing this nine to five, but I am pretty busy with it.
I used to write letters to the editor [at journals], but it’s a very infuriating process. So, it’s through getting frustrated that I discovered PubPeer.
You recently left your 2,000th comment on PubPeer. What keeps you coming back?
I enjoy the ridiculous back and forth with the authors over e-mail. I care a lot about the animals [that are killed for life-sciences experiments] as well. The level of expectation we should have when we’re dealing with animals and high-profile institutions is that they’re super careful and that they get things right, so it’s frustrating when you see errors.
What’s your usual process when you’re combing through a paper?
It’s going to depend on the problem that I might expect to find. A few months ago, [the open-access journal] PLoS One retracted nine papers, and these were all to do with gastric-damage stuff. In that case, I was looking for image reuse between papers. I went and I got all of this guy’s papers, and I cropped all of the images out of all the papers, put it in a giant folder and then resized them all. And I used a script to feed it into Imagetwin [software that compares images with a database of more than 25 million others]. But for the DFCI stuff, a lot of what I found and what had been previously posted [on PubPeer] is duplicated images within the same paper. Imagetwin is really useful for these things.
I note and collect the errors on PubPeer, write a blog, send the blog to the publisher and university. What I’m hoping for is that the authors respond on PubPeer. If I see a really credible, active response on PubPeer, then I’d probably just leave it there.
Thinking about the DFCI papers, what pattern of potential image manipulation stood out to you the most?
There is one where there’s images of mice, and it looks like one of them has been copied lots of times, and there’s a bioluminescent signal that’s been superimposed on top. It’s got the ears in the same place. It’s almost certainly the same mouse in about five different pictures in different groups and different time points. In [another paper], you’ve got a western-blot figure, and the same band has appeared multiple times across the whole lot. Not just one splice or one clumsy copy and paste; it’s the same band that has been superimposed into that block quite carefully.
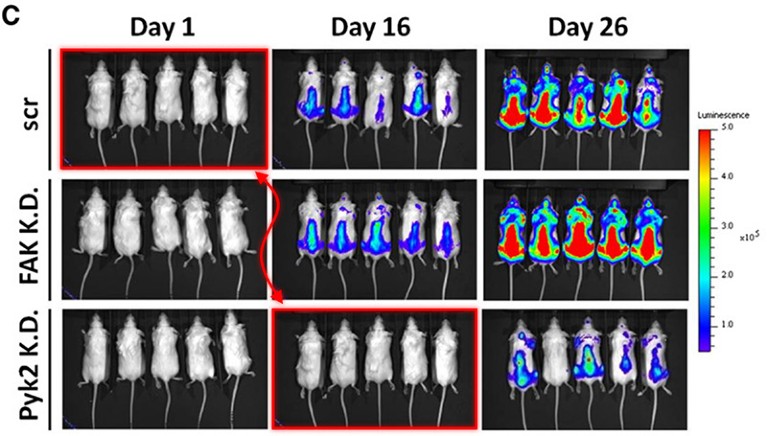
In his 2 January blogpost, David flagged research manuscripts containing images of mice that seem to have been copied and pasted.Credit: Annotation of Figure 2C (Y. Zhang et al. Blood 124, 2675–2686; 2014) by Sholto David
What did you think of the DFCI’s acknowledgement that it would seek retractions for 6 papers and corrections for 31 others?
I’ve flagged about 58 papers. In 16 or 17 of those, they say the data was collected at other institutions. Three of them, they dispute. I accept that. But I’d like to know what the dispute is. [The DFCI did not respond to explain why it disagrees with the anomalies flagged by David. It also said that one further paper is still under examination.]
So that seems like it’s pretty much all of them accounted for. In one sense, I’m relieved. They basically accepted that these are all errors. I stand by what’s on the blog and by what I post on PubPeer.
It does leave a frustrated feeling because a lot of these comments have been on PubPeer for ages. But now, suddenly, after the blogpost, Rollins has said, ‘we’ve known about some of these concerns’. Why does it take some nobody like me dropping a blog to make them start doing this? [Berlin didn’t immediately respond to questions on when the DFCI’s investigation began or how many papers the institute was investigating before David published his blogpost.]
Do you think journals are doing enough to correct the scientific record when these cases come up?
The response is usually slow, if they respond at all. It’s a very painful process to try to report an accusation of image duplication. It’d be nice if there was an obvious way just to click a button and flag a paper. It would be nice if you could leave a comment on the journal’s page, because how many people read PubPeer?
How can scientists avoid accusations of data impropriety?
There’s a pretty simple way to preventing all of this: you should design some file-organizing system that involves giving research images a sensible name. And then when it comes to checking your paper before you publish it, you need to trace back all the images to the raw data and check them against the metadata. For example, if you have a photo labelled as ‘Day three’, does that correspond to the date the photo was taken or that the experiment happened on?
Do you have any recommendations for scientists whose work is questioned?
I don’t want to make an environment where people feel harassed. The main thing I’d like to see is a polite response, and to acknowledge whether the error is there or not. Because it’s very frustrating if you say, ‘We’ll look into this,’ without acknowledging the errors on the page or giving a timeline.
Nature 626, 16-17 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00202-9
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.