海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月

氢是最有前途的燃料之一,可以满足日益增长的能源需求。目前使用的制氢方法大多不够环保,还会释放各种形式的污染物。光催化水分解法被认为是真正的 “绿色产氢”方法。传统上,光催化剂是基于块状氧化物材料,如TiO2。而较大的带隙、较低的可见光收集率以及较高的电荷复合程度限制了它们的广泛应用。近来人们发现多种二维(2D)材料可用于光催化,其中过渡金属硫属化合物和碳氮化物已被广泛研究。2D层状双氢氧化物(LDH)也是一类值得关注的具有良好光催化材料,具有八面体对称群(Oh)或1T相,其中六个羟基配体(OH−1)与八面体中心的金属原子相连。然而经数年研究也没有找到一种产氢性能超群的光催化材料。更重要的是,通过计算或实验手段在广阔的化学空间中手工寻找有前景的材料耗时、费力、乏味。
印度科学研究所材料研究中心的Abhishek K. Singh教授领导的团队,将可解释的机器学习(iML)和高通量方法相结合,用以寻找高效的二维水分解光催化剂 (2DO)。高通量方案的第一层包括选择具有高热力学和动力学稳定性的2DO材料。整体稳定性是根据强约束和适当规范(SCAN)计算的形成能和凸包距离,以及弹性刚度系数和Γ点声子来决定的。由于进行相关DFT计算所需的总计算时间约为3年或45万CPU核·时,因此需要引入机器学习来加速筛选过程。对此,作者采用了包括平均特征排序和贝叶斯超参数优化在内的高精度机器学习方法,来预测形成能和凸包距离,并将整体稳定性分为九个等级。基于化学硬度的特征,迄今为止还没有在材料科学的机器学习应用中得到应用,而这种特征可同时实现元素特征的准确性和结构特征的可识别性。作者发现,具有化学键硬-软相互作用或软-软相互作用的2DO材料具有最佳的GW带隙,而硬-硬相互作用使其不适合吸收可见光。21种有前途的2DO光催化剂同时满足合适的带隙和能带排列要求。通过计算这21种2DO候选材料的太阳能制氢效率,作者发现HfSe2和ZrSe2两种材料具有高达18%的效率,达到了理论极限。作者提出的利用元素和化学硬度特征的方法也可以应用于其它应用场景的新型材料的筛选设计。该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 7: 197 (2021),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。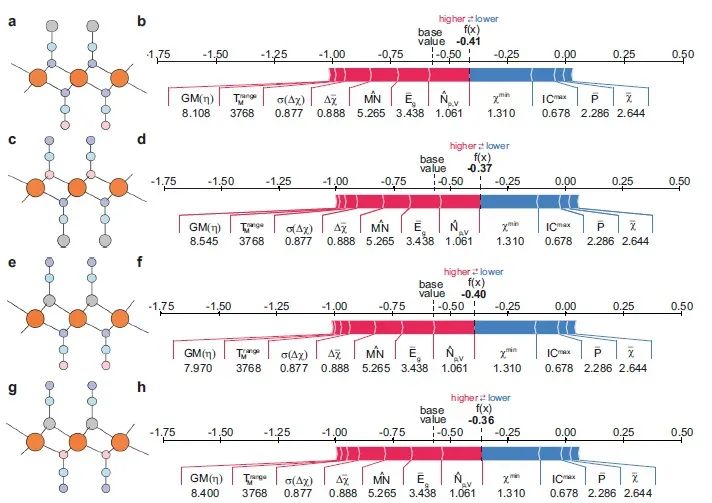
Chemical hardness-driven interpretable machine learning approach for rapid search of photocatalysts
Ritesh Kumar & Abhishek K. Singh
Strategies combining high-throughput (HT) and machine learning (ML) to accelerate the discovery of promising new materials have garnered immense attention in recent years. The knowledge of new guiding principles is usually scarce in such studies, essentially due to the ‘black-box’ nature of the ML models. Therefore, we devised an intuitive method of interpreting such opaque ML models through SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) values and coupling them with the HT approach for finding efficient 2D water-splitting photocatalysts. We developed a new database of 3099 2D materials consisting of metals connected to six ligands in an octahedral geometry, termed as 2DO (octahedral 2D materials) database. The ML models were constructed using a combination of composition and chemical hardness-based features to gain insights into the thermodynamic and overall stabilities. Most importantly, it distinguished the target properties of the isocompositional 2DO materials differing in bond connectivities by combining the advantages of both elemental and structural features. The interpretable ML regression, classification, and data analysis lead to a new hypothesis that the highly stable 2DO materials follow the HSAB principle. The most stable 2DO materials were further screened based on suitable band gaps within the visible region and band alignments with respect to standard redox potentials using the GW method, resulting in 21 potential candidates. Moreover, HfSe2 and ZrSe2 were found to have high solar-to-hydrogen efficiencies reaching their theoretical limits. The proposed methodology will enable materials scientists and engineers to formulate predictive models, which will be accurate, physically interpretable, transferable, and computationally tractable.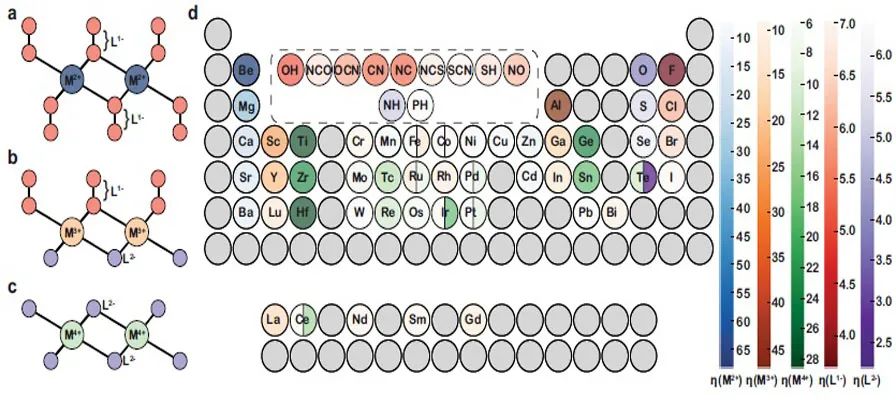
本文系网易新闻·网易号“各有态度”特色内容
媒体转载联系授权请看下方
